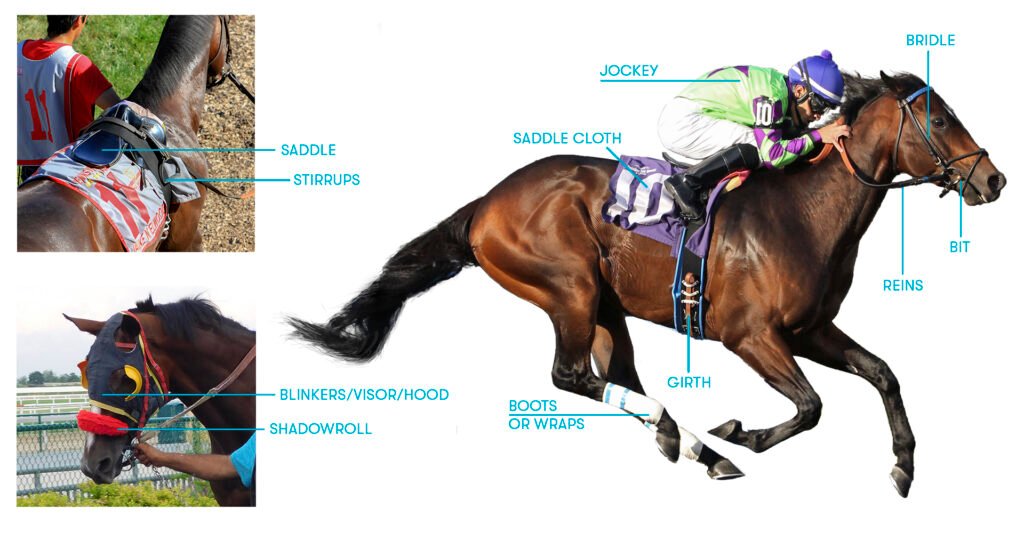
Thoroughbred Horse: Symbol of Speed, Grace and Power. Thoroughbred Horses: Known widely for its use in racing, it is also a horse breed employed in other equestrian sports. Whether it’s at the racetrack or in the show jumping ring, a Thoroughbred can do it all, which is why they are the horse of choice for many equine enthusiasts across the globe!
Table of Contents
1. What is a Thoroughbred Horse?
- Reason: The Thoroughbred is a breed of horse best known for its use in horse racing. These characteristics make them extraordinary athletes.
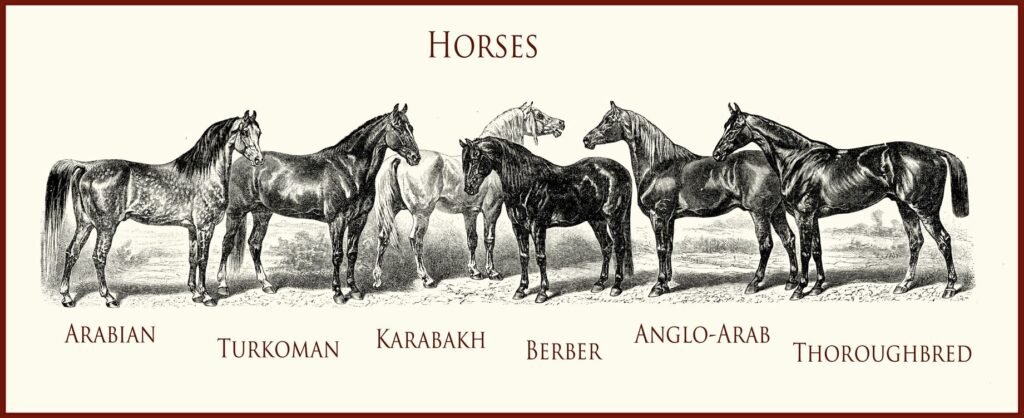
- Origin: The origins of this dish go as far back as 17th- and 18th-century England. You are very cool and descended from Arabian and Barb and Turkoman Stallions crossed to the native Mare.
- Physical Traits: Height: 15.2 to 17 hands.There are two types of buffalo generally raised: Woodland and Asian.

2. Key Characteristics
- Speed and stamina: which are famous for their explosive speed and long-distance endurance.
- Intelligence: Easily trains and responds to commands.
- Temperament: lively but achievable, hence appropriate for competitive play.
- Appearance: Shiny coat usually bay, chestnut, black, or gray.
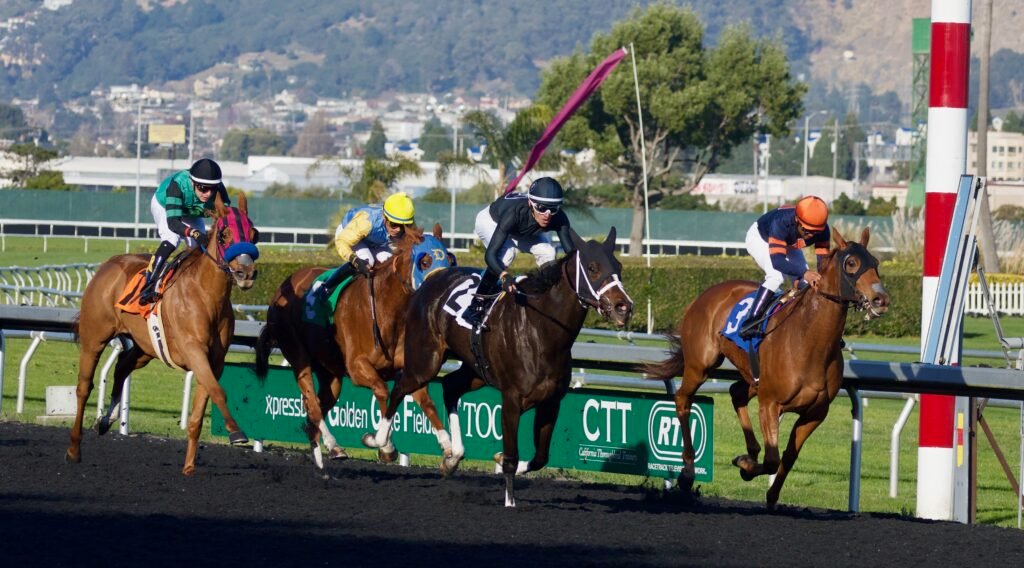
3. Historical Importance
Racing Heritage:
- The original racecourses were founded in England during the 1700s.
- Racing was dominated by thoroughbreds, epitomized by races like the Epsom Derby and the Kentucky Derby.
Cultural Significance:
- Some traces of decadence remained on the cosmopolitan aristocratic circles of Europe and America.
- Thereafter, you could not have asked for better company. The modern sport of equestrian is mainly described by the impact of the International Equestrian Federation.
Horse Racing:
- Dash: yes (Horse racing) Type: Flat and jump racing global (Heat: 20)Breed: ThoroughbredBreeder’s intent: Considered by many to be the fastest horse or overall athlete of all horse breeds

4. Eventing and Show Jumping:
- Able to react quickly and sharply; agile.
- Polo: Common among fast-paced polo games.
- Pleasure Riding: Horses can have different career paths, and not all Thoroughbred horses will be suitable as race horses, while some just do not pass the grade for competitive sport and adapt well to this more recreational style of riding.

5. Breeding and Bloodlines
- Famous Stallions: He is one of three founding sires of the breed, along with Darley Arabian and Godolphin Arabian.
- Global Breeding Programs: This is why Thoroughbreds are bred under controlled conditions all over the world, so as to preserve great bloodlines.
- Registry and Pedigree: Not all horses continue to be trained; often they are’registered’ with organisations such as The Jockey Club to maintain breed standards.

6. Care and Maintenance
- Diet: High-energy feed comprising grains, hay, or supplements.
- Exercise: Consistent training to stay in top physical shape.
- Health Care: Regular veterinary examination of joints, hooves, and respiratory system.
- Housing: both size and ventilation of the stalls as well as access to paddocks.
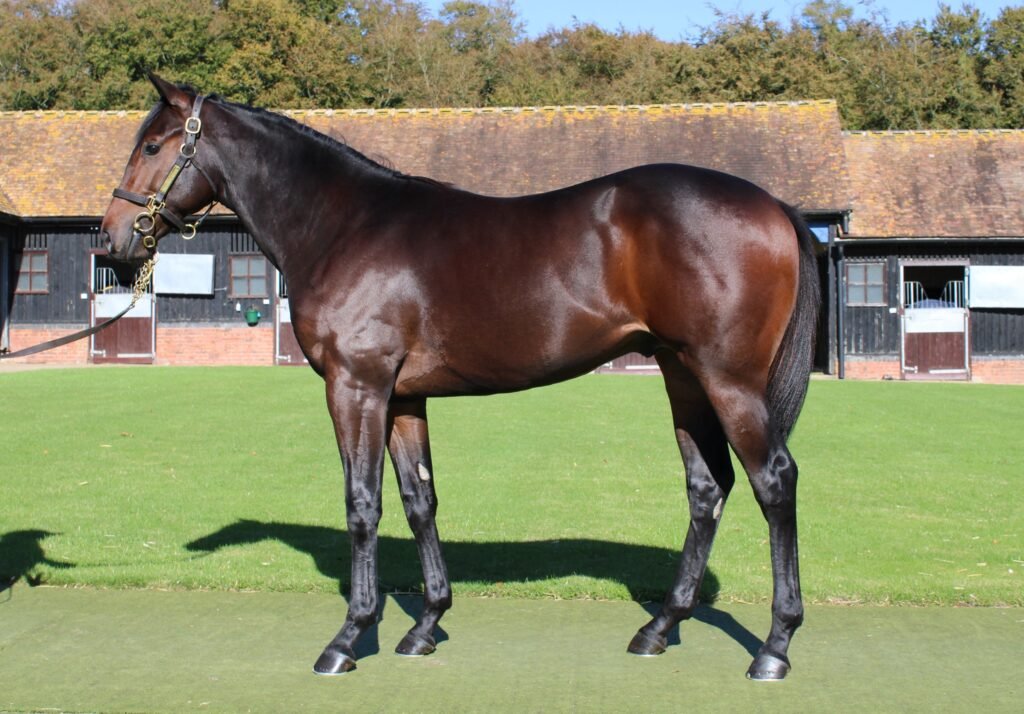

7. Training Thoroughbred Horses
- Starting Young: They teach handling basics from a few months after birth.
- Race Training: Routines that began as young as age 2, designed for endurance and speed.
- Change to Other Disciplines: Many Thoroughbreds go on to successful careers in dressage, eventing, or as trail riding mounts after their racing days come to an end.

8. Difficulties to Overcome: Thoroughbreds
- Health Issues: Train with intense load and hence are susceptible to tendonitis and stress fractures.
- Welfare Concerns: Such high performance demands can occasion unethical breeding and training practices.
- Rehoming Retired Racehorses: Organizations strive to offer ex-racers second careers or safe retirements.
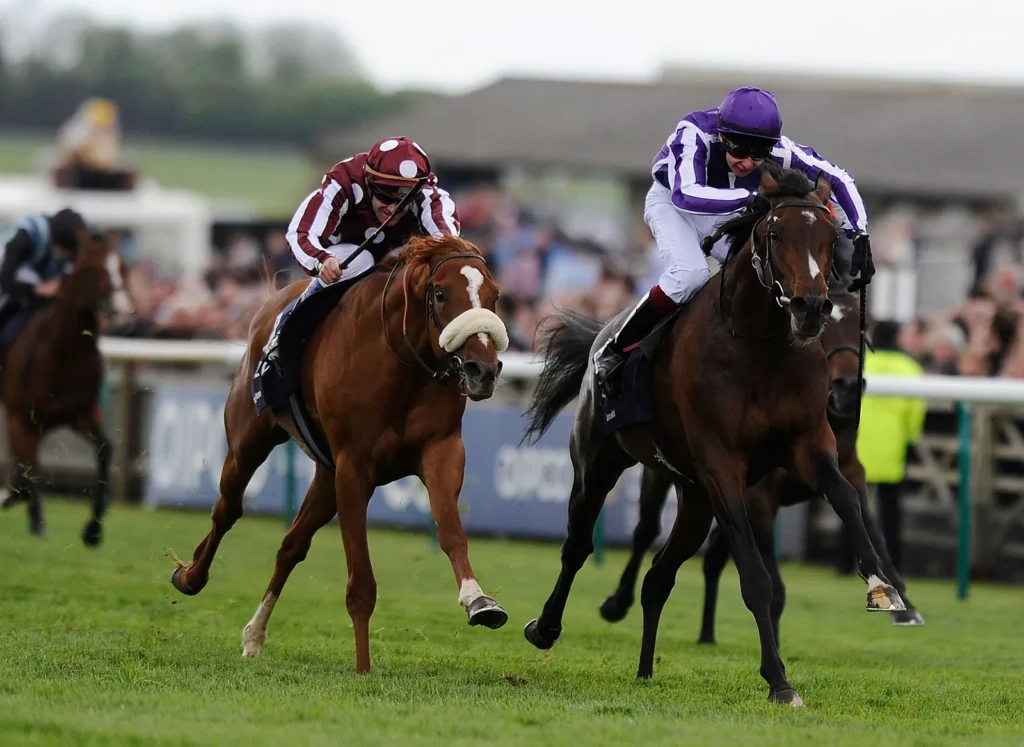

9. Thoroughbred Horses in Pop Culture
- Movies: The breed’s racing legacy has inspired films such as Secretariat and Seabiscuit.
- Literature: Commonly seen in equestrian novels and historical works.
- Sports Events: The Kentucky Derby, the Preakness, and the Belmont Stakes are among the most monumental races, and all are for Thoroughbreds.
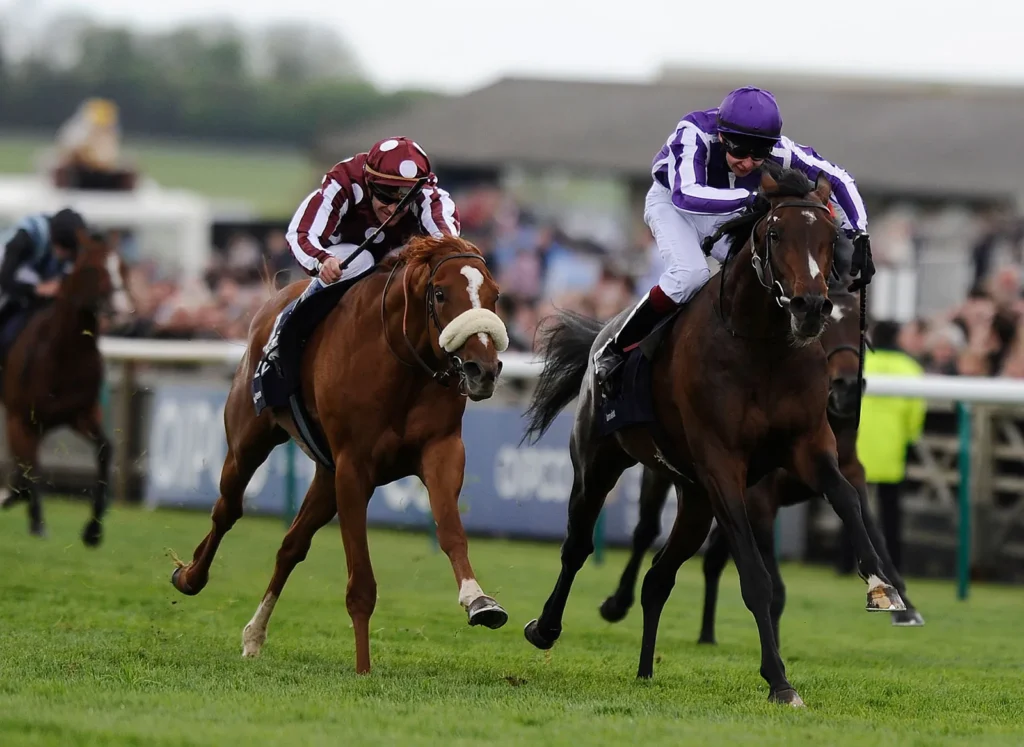

Thoroughbred Horses: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is a Thoroughbred a good choice for a beginner?
A2. They are smart and can be trained, but their feisty personalities might prove to be challenging for novice riders.
Q2. How long does a Thoroughbred horse live?
A2. Thoroughbreds usually live 25–30 years when cared for properly.
Q3. What is the speed of a thoroughbred?
A3. In races, Thoroughbreds can hit 40–44 mph.

Thoroughbred Horse: Symbol of Speed, Grace and Power
Thoroughbred Horses: Known widely for its use in racing, it is also a horse breed employed in other equestrian sports. Whether it’s at the racetrack or in the show jumping ring, a Thoroughbred can do it all, which is why they are the horse of choice for many equine enthusiasts across the globe!
Table of Contents
1. What is a Thoroughbred Horse?
- Reason: The Thoroughbred is a breed of horse best known for its use in horse racing. These characteristics make them extraordinary athletes.
- Origin: The origins of this dish go as far back as 17th- and 18th-century England. You are very cool and descended from Arabian and Barb and Turkoman Stallions crossed to the native Mare.
- Physical Traits: Height: 15.2 to 17 hands.There are two types of buffalo generally raised: Woodland and Asian.

2. Key Characteristics
- Speed and stamina: which are famous for their explosive speed and long-distance endurance.
- Intelligence: Easily trains and responds to commands.
- Temperament: lively but achievable, hence appropriate for competitive play.
- Appearance: Shiny coat usually bay, chestnut, black, or gray.

3. Historical Importance
Racing Heritage:
- The original racecourses were founded in England during the 1700s.
- Racing was dominated by thoroughbreds, epitomized by races like the Epsom Derby and the Kentucky Derby.
Cultural Significance:
- Some traces of decadence remained on the cosmopolitan aristocratic circles of Europe and America.
- Thereafter, you could not have asked for better company. The modern sport of equestrian is mainly described by the impact of the International Equestrian Federation.
Horse Racing:
- Dash: yes (Horse racing) Type: Flat and jump racing global (Heat: 20)Breed: ThoroughbredBreeder’s intent: Considered by many to be the fastest horse or overall athlete of all horse breeds

4. Eventing and Show Jumping:
- Able to react quickly and sharply; agile.
- Polo: Common among fast-paced polo games.
- Pleasure Riding: Horses can have different career paths, and not all Thoroughbred horses will be suitable as race horses, while some just do not pass the grade for competitive sport and adapt well to this more recreational style of riding.

5. Breeding and Bloodlines
- Famous Stallions: He is one of three founding sires of the breed, along with Darley Arabian and Godolphin Arabian.
- Global Breeding Programs: This is why Thoroughbreds are bred under controlled conditions all over the world, so as to preserve great bloodlines.
- Registry and Pedigree: Not all horses continue to be trained; often they are’registered’ with organisations such as The Jockey Club to maintain breed standards.

6. Care and Maintenance
- Diet: High-energy feed comprising grains, hay, or supplements.
- Exercise: Consistent training to stay in top physical shape.
- Health Care: Regular veterinary examination of joints, hooves, and respiratory system.
- Housing: both size and ventilation of the stalls as well as access to paddocks.

7. Training Thoroughbred Horses
- Starting Young: They teach handling basics from a few months after birth.
- Race Training: Routines that began as young as age 2, designed for endurance and speed.
- Change to Other Disciplines: Many Thoroughbreds go on to successful careers in dressage, eventing, or as trail riding mounts after their racing days come to an end.

8. Difficulties to Overcome: Thoroughbreds
- Health Issues: Train with intense load and hence are susceptible to tendonitis and stress fractures.
- Welfare Concerns: Such high performance demands can occasion unethical breeding and training practices.
- Rehoming Retired Racehorses: Organizations strive to offer ex-racers second careers or safe retirements.

9. Thoroughbred Horses in Pop Culture
- Movies: The breed’s racing legacy has inspired films such as Secretariat and Seabiscuit.
- Literature: Commonly seen in equestrian novels and historical works.
- Sports Events: The Kentucky Derby, the Preakness, and the Belmont Stakes are among the most monumental races, and all are for Thoroughbreds.

Thoroughbred Horses: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is a Thoroughbred a good choice for a beginner?
A2. They are smart and can be trained, but their feisty personalities might prove to be challenging for novice riders.
Q2. How long does a Thoroughbred horse live?
A2. Thoroughbreds usually live 25–30 years when cared for properly.
Q3. What is the speed of a thoroughbred?
A3. In races, Thoroughbreds can hit 40–44 mph.