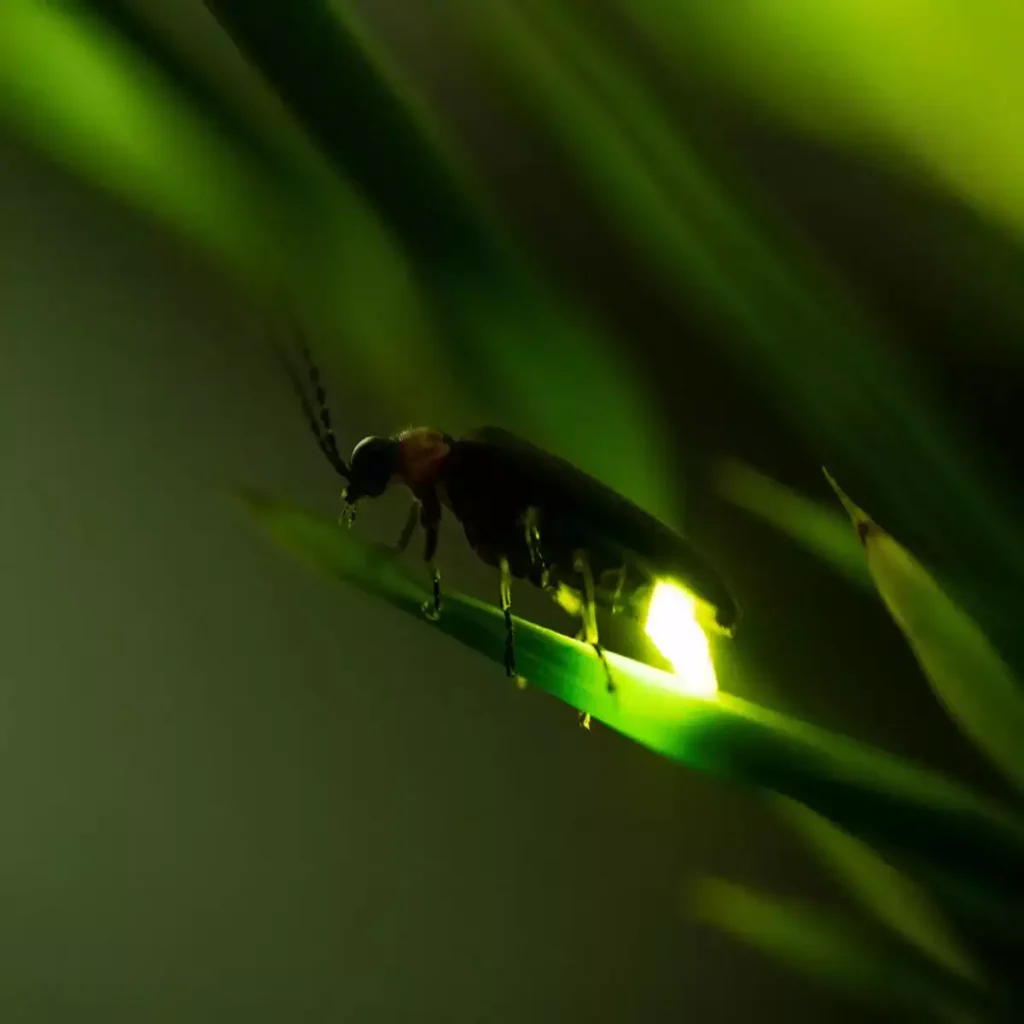
The soft light insect of the world seems yet to come alive in the dark, mysterious hours of night. This beautiful phenomenon takes place during natural wonders when light-producing insects fly around and emit flashes of bright lights or trails.
“From fireflies dancing in the summer air to glowing bioluminescent beetles that illuminate darkened woods, light insects are among the most enchanting creatures on the planet,” said a science communication researcher at Washington State University. But what are light insects, and how do they put on such a dazzling show?
In this blog, we will explore the science behind these amazing creatures, their role in nature and some of their awesome abilities.
Table of Contents

What Are Light Insects?
- Light insects Any insect with the ability to emit light or produce bioluminescence. Bioluminescence — the production and emission of light by living organisms is most commonly linked to some species of fungi, bacteria and marine animals. Nonetheless, a small number of insects share this uncanny skill.
- Several insect families are bioluminescent, but the most familiar are fireflies (or lightning bugs), glowworms, and some beetles such as click beetles. Here is a chemical reaction that the insect produces light; it involves specialized cells known as photocytes.
- The light that these insects emit is typically a gentle, pale yellowish, green or bluish radiance. It is cold light, meaning that it emits little or no heat “high efficiency” bioluminescence. Such a glow is beautiful and energy-efficient.
How Do Insects Light Up Thessaly’s?
Bioluminescence in insects (including fireflies) is a chemical reaction involving a molecule called luciferin and an enzyme named luciferase. The essential chronology of events is as follows:
- Luciferin: The compound responsible for light production upon oxidation.
- Luciferase: The enzyme that accelerates the reaction.
- Oxygen: It’s a requirement for the reaction to take place.
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): It serves as an energy source that is required to power the process.
When an insect’s phorocytes (specialized light-producing cells) are signalled to do so by the nervous system, luciferin reacts with oxygen under the influence of catalysing luciferase enzyme and bupkis light is produced. The light produced from this reaction is generally within the visible light spectrum.
The light is generated in pulses or patterns, which helps explain why fireflies, for instance, are often spotted flashing in the dark. Different species have varying intensity, color and frequency of these light patterns, which are often used for communication and reproduction.

Why Do Insects Glow?
- Bioluminescence among insects is thought to serve different purposes, depending on the species. Here are some reasons why light insects emit light, based on more common forms:
- Courtship Displays: One of the most famous usages of bioluminescence within insects is for courtship.
- Fireflies, for instance use their light to attract potential mates. Different kinds of fireflies produce different light patterns, and females generally respond to particular patterns.
- The males are flying and flashing their lights in a beat, calling attention to themselves as the females wait on the ground and flash back. It has yet been three months of coordinated display, which only members of the same species will mate.
- Predator Avoidance: Some firefly-like insects use their bioluminescence as a form of defence. The bright light may act as a warning to predators by indicating that the insect is toxic or unappetizing, experts say.
- This phenomenon is called aposematism a survival tactic whereby predators are informed by bright colours or patterns not to consume the creature. Some species of bioluminescent beetles, for instance, are unpalatable to potential predators and their light may help discourage attacks.
- Prey Attraction: Some species use bioluminescence as a means to lure in prey as well. Some glowworms, for instance, exude a bluish-green light to lure smaller creatures who are then snared in sticky silk threads.
- Since the glowworm’s food is usually in the nearby area, the light acts as an irresistible attraction to it, making certain that it’ll catch a meal.
- Blending in: Some bioluminescent insects use their light for camouflage, blending into their environment even more and making it harder to be seen by predators.
- With some fireflies and glowworms, the soft glow might enable them to blend into moonlight or starlight and thus reduce their chance of discovery by nocturnal predators.

Types of Light Insects
- Fireflies (Family Lampyridae): One of the most recognizable light bugs is maybe firefly, member of a family found all-over the world including North America and some parts of Asia and Europe.
- Fireflies are part of the beetle family Lampyridae, with more than 2,000 species worldwide.
- The best-known species, Photinus spiralis, lives in the United States and displays dazzling patterns that illuminate summer nights.
- Fireflies are known for their courtship behavior, and the males flash certain patterns while the females respond by marking themselves with light.
- No two species of fireflies flicker in exactly the same way, and these differences help each species to recognize its own kind and attract mates.
- Glowworms (Family Lampyridae): Fireflies are almost exclusively nocturnal, but luminescent beetles are commonly called glowworms in their larval state.
- Glowworms live in moist areas like caves or forests.
- Glowworms emit light to attract prey, which they capture in silk threads that they create.
- The light comes from the bodies of the larvae, producing a nearly ethereal, starlike effect in its habitat.
- Click Beetles (Family Elateridae) Along with fireflies, click beetles are another group of organisms capable of light production.
- Though not as famous as the firefly, click beetles also use bioluminescence to communicate or attract mates.
Characteristic green or yellow light.
- Apart from bioluminescence, click beetles are well-known for their capacity to construct a clicking sound which assists them in swinging themselves upright when turned onto the backs.
- Railroad Worms (Family Phengodidae): Railroad worms are a kind of beetle whose name derives from the visual arrangement of their glowing segments that makes them appear like lights from a train moving down a railroad track.
- These beetles are particularly interesting because they produce different colours of light along their bodies for example, greenish-yellow at the front portion and red towards the rear.
- This glow in the dark is believed to assist with communication and even allows them to ward off predators.

Trained on data
- Bioluminescent insects are an important part of their ecosystems, despite their small size. Their light-generating capabilities sustain the equilibrium of numerous biological activities:
- Pollination: Several bioluminescent insects, such as some firefly species, are pollinators. When they attract other insects with their specific light, they contribute to the fertilization of plants, which in turn helps them breed and produce fruit and seeds. The fluttering of fireflies in particular — whom love to enhance circulation search for partners but are courted by the plants and flowers that they search where victory can result in root cross-born pollination.
- Light insects themselves are an important food source for many other creatures. Fireflies and other bioluminescent species are important members of the food web: Birds, amphibians and even larger insects eat them. And they serve as food for predators in nocturnal systems.
- Light insects: Fireflies and glowworms are sensitive to pollution, habitat destruction and climate change. Because their numbers can reflect broader environmental issues that affect the ecosystems in which they exist, warblers also make a great indicator species. The decline of fireflies, for example, has been associated with habitat fragmentation and light pollution.
Conservation and the Future of Photopic Invertebrates
Light insects are both beautiful and fascinating, but they have many threats. Climate change, habitat destruction, light pollution and pesticide use all threaten bioluminescent insects. Urban lights, on the other hand, can disrupt fireflies’ communication systems, making them less effective at finding love. Similarly, the destruction of forests and wetlands leaves fewer viable habitats for glowworms and other bioluminescent species.
They are doing everything possible to salvage these incredible insects. Some conservationists are campaigning to limit light pollution by using outdoor lighting more responsibly, while others focus on protecting natural habitats that sustain bioluminescent insects. Whether through studying the ecosystems light insects inhabit or figuring out how to protect those habitats, their glow is something all future generations should enjoy.

FAQs about Light Insects:
Q1. How Insects Of Light Produce The Light?
A1. The light of light insects originates in a chemical reaction with luciferin, luciferase, oxygen and ATP. It does so in unique cells called phorocytes, generating light without much heat.
Q2. Why do fireflies glow?
A2. Fireflies on the other hand, emit light most of the time during reproduction. Males flash light in precise ways, and females return blinking patterns.